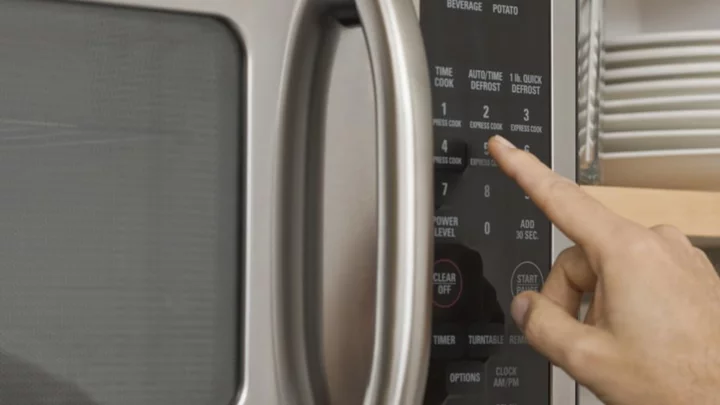

The Mesh Grating on Your Microwave Is Actually an Important Safety Feature
To block microwave radiation, all you need is a simple screen.
2023-09-08 23:20

OpenAI CEO Sam Altman First Person to Get Indonesian Golden Visa
OpenAI Chief Executive Officer Sam Altman is the first person to get an Indonesian golden visa as Southeast
2023-09-05 11:54

Spy attire: US investing $22m in surveillance socks and other wearable tech
The federal government is reportedly investing at least $22m into developing clothes that “can record audio, video, and geolocation data.” According to a 22 August press release from the office of the Director of National Intelligence’s Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity (IARPA), the research and development arm of the organisation, “recently launched a cutting-edge program that aims to make performance-grade, computerized clothing a reality”. The DNI touted the SMART ePANTS program, which stands for Smart Electrically Powered and Networked Textile Systems, that “seeks to develop clothing with integrated audio, video, and geolocation sensor systems that feature the same stretchability, bendability, washability, and comfort of regular textiles,” IARPA stated. They will be used by the intelligence community, IARPA wrote. Since the surveillance technology will be woven into the clothing, “Intelligence Community staff will be able to record information from their environment hands-free, without the need to wear uncomfortable, bulky, and rigid devices.” For example, according to the release, the technology could “assist personnel and first responders in dangerous, high-stress environments, such as crime scenes and arms control inspections without impeding their ability to swiftly and safely operate.” The SMART ePANTS program’s mission is to to incorporate “sensor systems” into clothes, like shirts, pants, socks, and underwear. The Intercept reported that the federal government has dedicated at least $22m in funding to the program. It’s unclear just how big of a gamble IARPA might be making with its investment. Its website describes itself as investing “federal funding into high-risk, high-reward projects to address challenges facing the intelligence community.” “A lot of the IARPA and DARPA programs are like throwing spaghetti against the refrigerator,” Annie Jacobsen, author of a book called The Pentagon’s Brain about ​​the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, told the outlet. “It may or may not stick.” Dr Dawson Cagle, an IARPA program manager leading the SMART ePANTS program, said that while he is “proud of the intelligence aspect” of the program, he’s “excited about the possibilities that the program’s research will have for the greater world.” He said that he was inspired in part to create the program by his father, who was a diabetic, and therefore had to monitor his health multiple times a day. His father’s experience paired with the research that supports that the components of a computer “have already been developed, just as individual pieces,” he explained. If you can convert all of the components into a single, wearable device, the program’s goal will have been achieved, Dr Cagle said. Ms Jacobsen warned that the advancement of smart wearables could lead to future concerns over biometric surveillance by the government. “They’re now in a position of serious authority over you. In TSA, they can swab your hands for explosives,” Ms Jacobsen told The Intercept. “Now suppose SMART ePANTS detects a chemical on your skin — imagine where that can lead.” But IARPA pushed back on this assertion, as spokesperson Nicole de Haay told the outlet: “IARPA programs are designed and executed in accordance with, and adhere to, strict civil liberties and privacy protection protocols. Further, IARPA performs civil liberties and privacy protection compliance reviews throughout our research efforts.” Read More Swedish citizen goes on trial on charges of collecting information for Russia Seoul's spy agency says Russia has likely proposed North Korea to join three-way drills with China Biden says he is ‘disappointed’ at Xi Jinping skipping India’s G20 summit Vodafone users say they can’t call people World’s first solar-powered hybrid truck tested on public roads Apple is about to make a huge change to the iPhone that it never wanted to do
2023-09-05 06:17

How to watch Louisville vs. Georgia Tech without ESPN on Spectrum
Friday night's Louisville vs. Georgia Tech game won't be available for Spectrum customers on ESPN because of a contract dispute with Disney. Here's how to watch without cable.
2023-09-02 06:57
Scientists believe they have found a cure for alcoholism
Alcohol addiction ruins millions of lives every year, but scientists may have found a cure for this terrible affliction. A new treatment for alcohol use disorder (AUD) has been trialled in monkeys with impressive results and, if these translate to human trials, the impact could be monumental. A team of neuroscientists and physiologists from across the US tested a new type of gene therapy to see if they could directly target the underlying brain circuitry associated with sustained heavy drinking. As they noted, in the journal Nature Medicine, people suffering from AUD commonly return to alcohol use even if they attempt to quit. This is largely to do with what’s known as mesolimbic dopamine (DA) signalling – meaning how the central nervous system circuit communicates the feelgood neurotransmitter dopamine. A protein called glial-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) is key to keeping these neurons in this reward circuitry functioning. However, experts have found that levels of GDNF are reduced in people with AUD during periods of alcohol abstinence, most notably in a region of the brain called the ventral tegmental area (VTA), as IFLScience notes. Therefore, the researchers decided to test whether using gene therapy to deliver more GDNF to the VTA could help reinforce this crucial dopaminergic signalling and prevent patients from suffering an alcoholic relapse. The team of scientists explained how alcohol consumption in non-addicts prompts the release of dopamine, creating a pleasurable buzz feeling, but chronic alcohol use causes the brain to adapt and stop releasing so much dopamine. “So when people are addicted to alcohol, they don’t really feel more pleasure in drinking,” Dr Kathleen Grant, a senior co-author of the study, said in a statement. “It seems that they’re drinking more because they feel a need to maintain an intoxicated state.” For their research, Dr Grant and her colleagues used eight rhesus macaque monkeys, who were exposed to increasing concentrations of alcohol over four 30-day “induction” periods. The monkeys then had free access to alcohol and water for 21 hours a day for six months, during which they developed heavy drinking behaviours. This was then followed by a 12-week abstinence phase, with the GDNF treatment performed four weeks in for half of the subjects. The gene therapy was delivered using a a viral vector containing a copy of the human GDNF gene injected directly into the primate’s VTA, according to IFLScience. And the results were truly jaw-dropping. “Drinking went down to almost zero,” Dr Grant said. “For months on end, these animals would choose to drink water and just avoid drinking alcohol altogether. They decreased their drinking to the point that it was so low we didn’t record a blood-alcohol level.” The most exciting aspect of their findings is the suggestion that gene therapy could offer a permanent solution for people with the most severe cases of AUD. This will be a welcome glimmer of hope to many, given that some 29.5 million people were diagnosed with AUD in the US alone in 2021, according to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Of these 29.5 million sufferers, almost a million (894,000) were aged between 12 and 17. It’ll likely be some time before we know for sure whether the gene therapy can be rolled out in humans, but it’s an important first step in tackling this devastating disorder. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-01 20:57

Disney Yanks ESPN Off Charter Cable Ahead of Football Season
Walt Disney Co. said customers of Charter Communications Inc. can no longer watch its TV networks because of
2023-09-01 20:57
Scientists may have just found a cure for alcoholism
Alcohol addiction ruins millions of lives every year, but scientists may have found a cure for this terrible affliction. A new treatment for alcohol use disorder (AUD) has been trialled in monkeys with impressive results and, if these translate to human trials, the impact could be monumental. A team of neuroscientists and physiologists from across the US tested a new type of gene therapy to see if they could directly target the underlying brain circuitry associated with sustained heavy drinking. As they noted, in the journal Nature Medicine, people suffering from AUD commonly return to alcohol use even if they attempt to quit. This is largely to do with what’s known as mesolimbic dopamine (DA) signalling – meaning how the central nervous system circuit communicates the feelgood neurotransmitter dopamine. A protein called glial-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) is key to keeping these neurons in this reward circuitry functioning. However, experts have found that levels of GDNF are reduced in people with AUD during periods of alcohol abstinence, most notably in a region of the brain called the ventral tegmental area (VTA), as IFLScience notes. Therefore, the researchers decided to test whether using gene therapy to deliver more GDNF to the VTA could help reinforce this crucial dopaminergic signalling and prevent patients from suffering an alcoholic relapse. The team of scientists explained how alcohol consumption in non-addicts prompts the release of dopamine, creating a pleasurable buzz feeling, but chronic alcohol use causes the brain to adapt and stop releasing so much dopamine. “So when people are addicted to alcohol, they don’t really feel more pleasure in drinking,” Dr Kathleen Grant, a senior co-author of the study, said in a statement. “It seems that they’re drinking more because they feel a need to maintain an intoxicated state.” For their research, Dr Grant and her colleagues used eight rhesus macaque monkeys, who were exposed to increasing concentrations of alcohol over four 30-day “induction” periods. The monkeys then had free access to alcohol and water for 21 hours a day for six months, during which they developed heavy drinking behaviours. This was then followed by a 12-week abstinence phase, with the GDNF treatment performed four weeks in for half of the subjects. The gene therapy was delivered using a a viral vector containing a copy of the human GDNF gene injected directly into the primate’s VTA, according to IFLScience. And the results were truly jaw-dropping. “Drinking went down to almost zero,” Dr Grant said. “For months on end, these animals would choose to drink water and just avoid drinking alcohol altogether. They decreased their drinking to the point that it was so low we didn’t record a blood-alcohol level.” The most exciting aspect of their findings is the suggestion that gene therapy could offer a permanent solution for people with the most severe cases of AUD. This will be a welcome glimmer of hope to many, given that some 29.5 million people were diagnosed with AUD in the US alone in 2021, according to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Of these 29.5 million sufferers, almost a million (894,000) were aged between 12 and 17. It’ll likely be some time before we know for sure whether the gene therapy can be rolled out in humans, but it’s an important first step in tackling this devastating disorder. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-31 19:54

Uber Eats’ New AI Chatbot Will Offer Recommendations to Customers
An artificial intelligence chatbot under development at Uber Technologies Inc. will offer recommendations to food-delivery customers and help
2023-08-29 02:58

Amazon, Warner Bros. Compete for New Package of Nascar TV Rights
Amazon.com Inc. and Warner Bros. Discovery Inc. are competing to broadcast a new package of Nascar races, with
2023-08-24 00:17
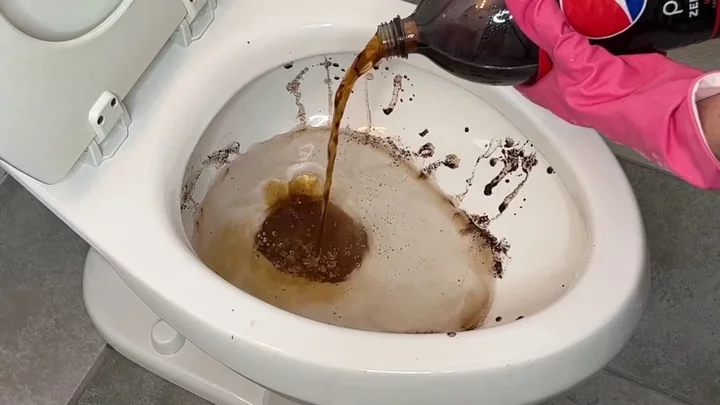

Toilet invented that is so slippy nothing can leave skid marks
A 3-D-printed toilet has been invented and the surface is so slippery that nothing can leave a mark on it. Cleaning the toilet has to be one of the grimmest household chores, but thanks to new material, you may never have to scrub a loo again. The toilet is the invention of Yike Li at Huazhong University of Science and Technology in Wuhan, China, who, alongside colleagues, invented a toilet whose surface is so slippery that nothing stains it and uses less water for each flush. The team created a prototype of the toilet around 10 times smaller than a real one. It was made using 3D printing technology, where particles of plastic and hydrophobic sand grains were fused together with lasers. The surface of the toilet was lubricated with a type of silicon oil that also penetrated the surface due to the complex structure of the material. The team tested the toilet with a variety of substances, including honey, yoghurt, muddy water as well as synthetic faeces. They found that none of the substances stuck to the toilet bowl. Amazingly, the toilet was just as slippery after having been rubbed with sandpaper over 1,000 times, which Li believes is due to the oil being able to penetrate the material of the toilet. Li believes the technology would be suited for settings in which a toilet gets a lot of use, such as on modes of transport and in public toilets. He explained: “The reduced flushing volume would result in less wasted water during transportation to the processing facilities, thereby saving transportation costs.” But, before that can happen, Li says the technology needs to be adapted for use on a full-sized toilet and also needs to be cheaper to make. You can see the toilet in action below courtesy of New Scientist. Nothing can stick to this 3D-printed slippery toilet youtu.be Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-22 20:24

Why you should delay your first coffee of the morning
For a lot of people, coffee is one of the few things that gets them out of bed and out the door in the mornings. But while it’s tempting to whack the kettle on first thing, a health expert has stated that delaying our first coffee of the day could be much more beneficial to our health. Nutritionist Gabi from The Fast 800 urged people to wait at least 90 minutes before getting their first coffee hit [via the Mirror]. Gabi claims that we can all boost energy levels by doing so. In fact, eating on an empty stomach could even cause your body to enter stress mode and release hormones like adrenaline and cortisol. "Supporting your morning coffee routine with some smart practices can be a game changer for your overall well-being,” Gabi said. She recommends drinking water, as well as eating a meal packed with fibre and protein to balance sugar levels. “Elevated blood sugar can trigger inflammation and set us up to be on a blood sugar roller coaster for the rest of the day, thereby tanking our energy supply,” the health guru said. "Within the first hour of waking, our cortisol levels ideally acutely rise and fall in a response known as our cortisol awakening response. This rise and fall of cortisol represents a healthy nervous system and actually has a big influence on our immune health and even the risk of autoimmune development." She also states that delaying coffee for a minimum of 90 minutes promotes high energy levels. Gabi said: "Morning light exposure is a huge regulator of circadian rhythm and light exposure triggers the healthy release of cortisol in the morning to support the body’s natural rhythm. Getting natural light exposure within the first hour or so of waking is a great way to support optimal hormone balance." It comes after it was revealed that the drink also gives us an extra ‘special boost’ as well as just a caffeine hit. Scientists have claimed that the act of drinking a cup of joe gives the body a lift, making us more alert, which can’t be replicated merely with caffeine. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-21 17:18

Social media firms should reimburse online purchase scam victims – Barclays
Tech companies should help to reimburse the victims of social media purchase scams, bosses at Barclays have said. It comes as data from the bank revealed a jump in the number of social media scams affecting British shoppers. Purchase scams, where people buy good which never arrive or are not as advertised, now account for two thirds of all reported scams, according to the research. Barclays said that 88% of these scams, which cause victims to lose £1,000 on average, start on social media platforms. The bank has called for more to be done in order to prevent these scams, demanding further action from social media companies and politicians. It has called for a victim reimbursement fund to be financed by all firms whose systems and platforms are used to perpetrate scams, including tech companies and banks, as part of four recommendations. Currently victims are only reimbursed by funding from banks, Barclays said. The banking giant also called for the creation of a cross-Government group within the Home Office to deal with the issue in order to coordinate regulators, policy makers, industry groups, and companies across different sectors. The prevention of scams should also be made mandatory, particularly for tech companies, in a shift from current voluntary measures, it added. Barclays also urged the Government to make organisations publish their scams data in order to inform consumers of the risks involved in using their platforms. Matt Hammerstein, chief executive officer of Barclays UK, said: “With so much of everyone’s lives now being online, from staying connected with friends and family, to shopping, it’s important that people feel safe on the platforms they use. “Our data shows that tech platforms, particularly social media, are now the source of almost all scams. “However, there is no current legislative or regulatory framework obliging the tech sector to support the prevention of these crimes, as there rightly is for banks. “We can only drive back this epidemic, and protect UK competitiveness, by stopping scams at their source, preventing the flow of funds to organised crime.” Read More Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live Hozier would consider striking over AI threat to music industry Snapchat experiences ‘temporary outage’ as My AI chatbot posts own Story Crime victims’ data revealed by two police forces in FoI responses
2023-08-21 07:27
